dna strand definition
One strand is in the 5 to 3 direction with respect to the carbon atoms on the sugar deoxyribose and the complementary strand is in the 3 to 5 direction Figure 1 a. Nearly every cell in a persons body has the same DNA.
DNA is made up of millions of nucleotides.

. Each rung is made up of two chemical bases called nucleotides that are joined together by hydrogen bonds. These building blocks are made of three parts. It consists of two long strands linked together in a structure resembling a ladder twisted into a spiral called a double helix.
To form a strand of DNA nucleotides are linked into chains with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating. The very long molecule that winds up to form a CHROMOSOME and that contains the complete code for the automatic construction of the body. The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix.
Nucleotides in DNA are molecules made of deoxyribose sugar a phosphate and a nitrogenous base. But replication is discontinuous on the other template with polarity 5 to 3 because DNA polymerase enzymes can add nucleotides in. A section of one nucleic acid chain that is bonded to another by a sequence of base pairs.
The coding strand of DNA is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. What is meant by complementary DNA. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms.
Majority of DNA has a B type. The complementary DNA strand the one that is not used is called the nonsense or antisense strand. DNA strands are polymers or chains of deoxynucleoside monophosphates that are linked together by phosphodiester bonds Figure 1 a.
DNA is the chemical name for the molecule that carries genetic instructions in all living things. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme condition such as desiccation. The template strand is complementary to this and can be transcribed to.
In law the importance is the discovery that each persons DNA is different and is found in each living cell so a hair blood skin or any part of the body can be used to identify. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a complex molecule typically found in a cells nucleus that contains an organisms genetic information. The twisting gives the DNA its compactness.
Collins Dictionary of Biology 3rd. This is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix. Hence the DNA strand which consists of 3 to 5 directionality in the double-stranded DNA may serve as the template strand in transcription.
Complementary DNA cDNA is a DNA copy of a messenger RNA mRNA molecule produced by reverse transcriptase a DNA polymerase that can use either DNA or RNA as a template. Each strand has a sugar-phosphate backbone that is created when the phosphate of one nucleotide binds to the sugar. The DNA strands have the opposite orientation.
The two strands of. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus where it is called nuclear DNA but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA. DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides.
DNA is self-replicating plays a central role in protein synthesis and is responsible for the transmission of hereditary characteristics from. A DNA strand is a long thin moleculeaveraging only about two nanometers or two billionths of a meter in width. The molecule has a double helix skeleton of alternating sugars deoxyribose and phosphates.
It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. This mitochondrial DNA is more like bacterial DNAa single long circular piece of DNA made up of two strands of DNA. The double-stranded DNA molecule has two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape.
Either of the two chains that make up a double helix of DNA with corresponding positions on the two chains being composed of a pair of complementary bases. They found that DNA is a double-helical structure with two paired DNA strands with complementary nucleotide sequences. It is an important process to maintain and transfer genetic information from one generation to another.
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine A cytosine C. Nucleotides are arranged into chains that become individual strands of DNA which is half of a full DNA molecule. One strand with polarity 3 to 5 forms its complementary strand continuously and is called the leading strand.
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are of four types adenine guanine thymine and cytosine. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar deoxyribose and phosphate groups. That is so thin that a human hair is about 40000 times as wide.
A phosphate group a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. A DNA template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme DNA polymerases and RNA polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of DNA or at the time of transcription of RNA respectively. The strand in DNA replication that is synthesized continuously.
That means the template strand is the DNA strand in the double-stranded DNA which is responsible for the amino acid sequence of the synthesized polynucleotide chain. The phosphate and the deoxyribose sugars form a backbone-like. DNA polymerase works in pairs replicating two strands of DNA in tandem.
Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA and the DNA takes an A form. Scientifically deoxyribonucleic acid a chromonal double chain the famous double helix in the nucleus of each living cell the combination of which determines each individuals hereditary characteristics. Deoxyribonucleic acid commonly called DNA exists mainly in the nucleus and mitochondria of each cell in an organism.
The DNA strand grows in 53 direction by their polymerisation activity. The DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains in the form of a double helix containing phosphate and the sugar deoxyribose and linked by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. They add deoxyribonucleotides at the 3-OH group of the growing DNA strand.
DNA is usually a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides although single-stranded DNA is also known. See DNA SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION MODEL.

Enzymes In Dna Replication Dna Replication Science Biology Dna Research

Difference Between Sense And Antisense Strand Definition Characteristics Structure Basic Anatomy And Physiology Biology Facts Biochemistry Notes

Pin On What Are Dna And Dna Replication

Polymerase Chain Reaction Definition Steps In 2021 Molecular Biology Molecular Fields Of Science

Pin On Education 10 Biology Structure And Function Of Dna

Leading And Lagging Strands In Dna Replication Mcat Khan Academy Youtube Dna Replication Dna Dna Facts

Rna Polymerase Easy Science Rna Polymerase Science Flashcards Study Biology

Pin On What Are Dna And Dna Replication

Replication Fork Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Study Biology

Pin On What Are Dna And Dna Replication

Dna Replisome Replication Complex Dna Polymerase Dna Prokaryotes

Pin On Nucelotides Amino Acids Genes And Proteins

What Is 12 Strand Dna Activation Quantum Healing Hypnosis Dna Gene Expression
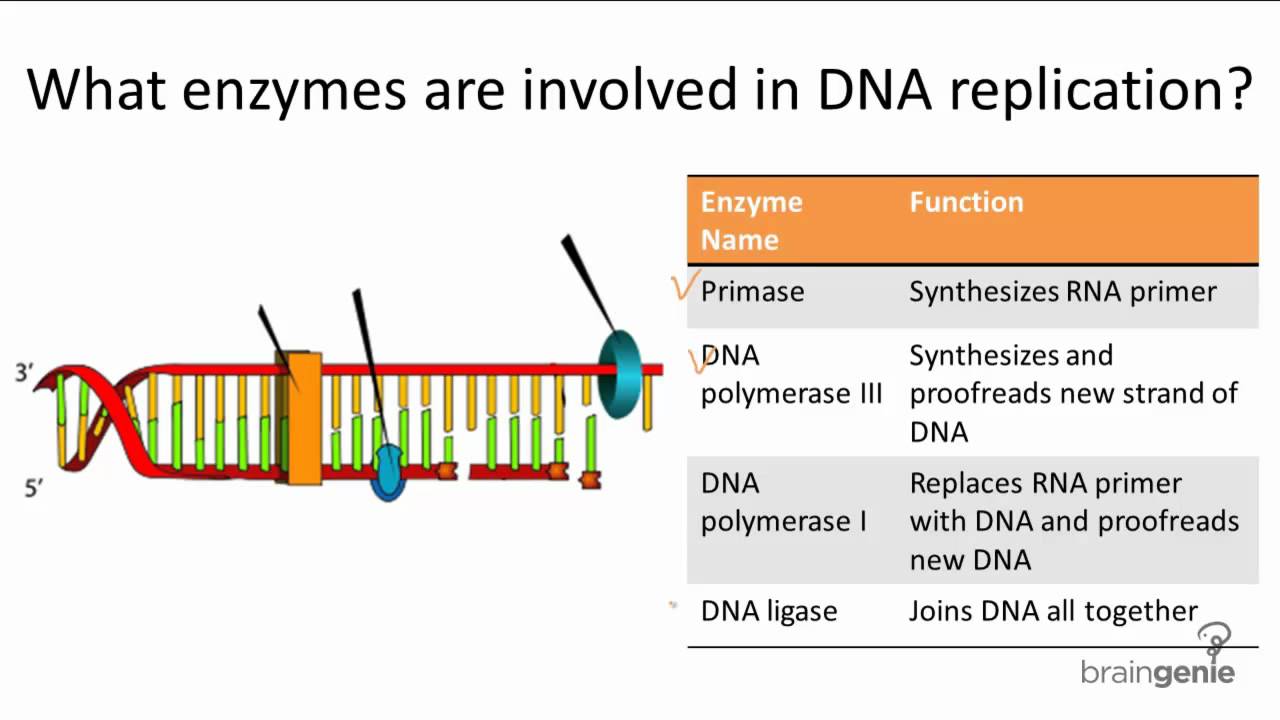
Image Result For Dna Replication And Enzymes Dna Replication Dna Ligase Dna

Picture Dna Replication Dna Polymerase Dna Replication Model

Single Stranded Binding Protein Ssbp Csir Net Life Sciences Dna Replication Dna Human Anatomy And Physiology

Difference Between Replication And Transcription Dna Replication Is The Process Of Making Two Daughter Str Study Biology Biology Lesson Plans Teaching Biology


Comments
Post a Comment